Multicomplex number
In mathematics, the multicomplex number systems Cn are defined inductively as follows: Let C0 be the real number system. For every n > 0 let in be a square root of minus one, that is, an imaginary number. Then 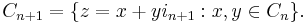 In the multicomplex number systems one also requires when n ≠ m that
In the multicomplex number systems one also requires when n ≠ m that 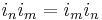 (commutative property). Then C1 is the complex number system, C2 is the bicomplex number system, C3 is the tricomplex number system of Corrado Segre, and Cn is the multicomplex number system of order n.
(commutative property). Then C1 is the complex number system, C2 is the bicomplex number system, C3 is the tricomplex number system of Corrado Segre, and Cn is the multicomplex number system of order n.
Each Cn forms a Banach algebra. G. Bayley Price has written about the function theory of multicomplex systems, providing details for the bicomplex system C2.
The multicomplex number systems are not to be confused with Clifford numbers (elements of a Clifford algebra), since Clifford's square roots of minus one anti-commute (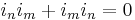 for Clifford). Furthermore, the multicomplex systems differ from the n-complex numbers introduced by Silviu Olariu in 2002. In particular, Olariu's tricomplex numbers differ from Segre's tricomplex numbers C3 defined above.
for Clifford). Furthermore, the multicomplex systems differ from the n-complex numbers introduced by Silviu Olariu in 2002. In particular, Olariu's tricomplex numbers differ from Segre's tricomplex numbers C3 defined above.
With respect to subalgebra Ck, k = 0, 1, ... n−1, the multicomplex system Cn is of dimension 2n−k over Ck.
References
- G. Baley Price (1991) An Introduction to Multicomplex Spaces and Functions, Marcel Dekker.
- Corrado Segre (1892) "The real representation of complex elements and hyperalgebraic entities" (Italian), Mathematische Annalen 40:413–67 (see especially pages 455–67).